Which Gas is Alphabetically First on the Periodic Table?
Table of Contents
ToggleWhich Gas is Alphabetically First on the Periodic Table?
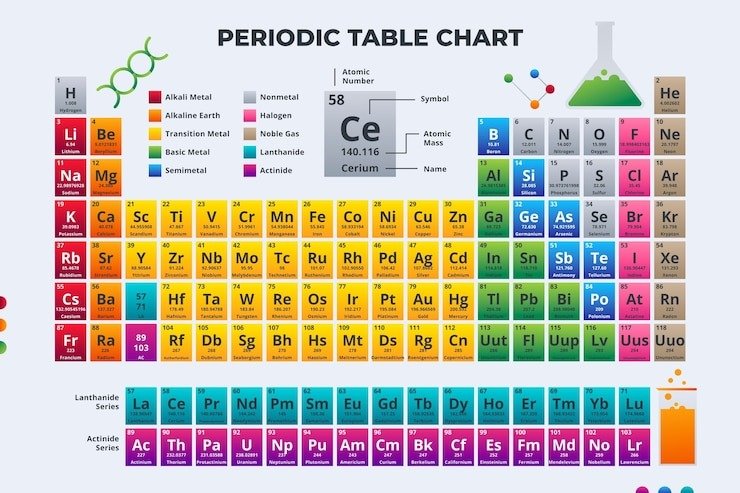
The periodic table organizes all known elements based on their atomic number, but if you were to arrange them alphabetically, you might be curious to know which gas appears first. The alphabetically first gas on the periodic table is Argon.
In this article, we will explore why Argon holds this position, its importance, and how understanding the alphabetical order of elements can provide a new perspective on the periodic table.
What is the First Gas Alphabetically?
The alphabetically first gas on the periodic table is Argon.
Argon is a noble gas with the atomic number 18. It is one of the six naturally occurring noble gases and is colorless, odorless, and non-reactive under standard conditions. As the third-most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, Argon constitutes approximately 0.93% of the atmosphere by volume. It is used in a variety of industrial applications, including welding, lighting, and in creating inert environments for scientific research.
While other gases like Helium and Hydrogen are often more well-known, Argon appears first when sorting elements alphabetically by their names.
Why is Argon Important?
Argon’s inert nature makes it particularly valuable in situations where chemical reactions need to be prevented. Its properties allow it to create stable environments in industrial processes, laboratories, and even inside double-pane windows, where it serves as an insulator.
Some of Argon’s most notable uses include:
- Welding: Argon gas creates an inert atmosphere during welding, which prevents oxidation and produces a clean weld.
- Lighting: In combination with other gases, Argon is used in fluorescent and incandescent lighting to produce a bright, clear light.
- Scientific Applications: Argon’s inert nature makes it suitable for various scientific experiments where non-reactivity is crucial, such as preserving historical documents or in gas chromatography.
Understanding Noble Gases and Their Alphabetical Order
Noble gases, also known as inert gases, are a group of elements that include Argon, Helium, Neon, Krypton, Xenon, and Radon. They are called “noble” because they are chemically stable and do not easily form compounds with other elements.
When listed alphabetically, the noble gases are ordered as follows:
- Argon (Ar)
- Helium (He)
- Krypton (Kr)
- Neon (Ne)
- Radon (Rn)
- Xenon (Xe)
Even though Helium is the second element in the periodic table in terms of atomic number, Argon comes first alphabetically due to the way it is spelled. This fact often surprises people because Helium is more well-known for its role in balloons and scientific research.
Why Knowing the Alphabetical Order of Elements is Interesting
While the periodic table is traditionally organized by atomic number and grouped by element properties, arranging it alphabetically can offer a fresh way to look at these chemical elements.
Understanding the alphabetical order of elements might not be necessary for most chemical studies, but it can be useful for:
- Quick Reference: Alphabetical organization can help students and scientists quickly find elements in large databases or research documents.
- Educational Tools: In teaching settings, using alphabetical order can help students memorize element names more easily, especially when creating mnemonic devices.
- Cross-Disciplinary Learning: For people outside of chemistry, such as historians or educators, the alphabetical order of elements might provide a simple framework for understanding the periodic table.
Comparison Between Argon and Other Gases
To provide a clearer understanding, let’s compare Argon with a few other gases from the periodic table:
| Gas | Atomic Number | Density (g/L) | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon | 18 | 1.784 | Welding, lighting, insulation |
| Helium | 2 | 0.178 | Balloons, scientific equipment |
| Oxygen | 8 | 1.429 | Breathing, combustion |
| Neon | 10 | 0.900 | Neon signs, high-voltage indicators |
From this comparison, it’s clear that Argon stands out for its industrial utility, especially in environments requiring inert atmospheres. While Helium is much lighter and more famous in everyday life, Argon’s applications are vital to many modern technologies.
Conclusion
Argon, the alphabetically first gas on the periodic table, holds a unique position not just in its ordering but also in its real-world applications. As an inert, stable element, Argon plays a key role in industries ranging from manufacturing to lighting.
While atomic number remains the standard way of ordering the periodic table, the alphabetical arrangement provides an interesting and useful perspective on the elements, helping learners and professionals alike.
Argon’s presence as the first gas alphabetically is just one example of how the periodic table can be explored in various ways, offering both educational value and practical insights into the nature of chemical elements.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is the alphabetically first gas on the periodic table?
The alphabetically first gas on the periodic table is Argon.
Q2: Why is Argon the alphabetically first gas?
Argon comes first alphabetically because its name starts with “A,” ahead of other gases such as Helium, Neon, and Oxygen.
Q3: What is Argon used for?
Argon is used in welding, lighting, insulation in double-pane windows, and scientific research where a non-reactive gas is required.
Q4: Is Helium the first gas alphabetically?
No, Helium is not the first alphabetically. Even though Helium is the second element by atomic number, Argon is first alphabetically.
Q5: How are gases typically arranged in the periodic table?
Gases, like all elements in the periodic table, are typically arranged by their atomic number, not alphabetically. However, for educational or quick reference purposes, elements can also be listed alphabetically.
Q6: What other noble gases follow Argon alphabetically?
After Argon, the next noble gases in alphabetical order are Helium, Krypton, Neon, Radon, and Xenon.
Q7: Why is alphabetical order important for elements?
Alphabetical order can make it easier to quickly reference elements, especially in educational tools, research databases, and for quick lookup.
Why You Need to Read These Blog
Which Gas is Alphabetically First on the Periodic Table?
A Complete Guide to Integrated Performance Assessment (IPA) in Language Learning
Deep Offshore Technology: Innovations, Challenges & Future Trends
Unlocking the Power of AI Content Creation: A Comprehensive Guide to Jasper AI
How to Plan an International Trip in Your Own Plane: A Complete Guide
Should You Search Google or Type a URL? Find Out the Best Approach
Top 5 Best Cheap Washing Machines and Dryers: Budget-Friendly Picks for 2024
What Is the Minimum Wage in Michigan 2024? Latest Rates & Updates
Top eCommerce Companies in Western PA: A Comprehensive Guide
What Travel Sites Accept PayPal?
Solar Panels vs Electricity Bills Savings in 2024: How Much Can You Save?
How to Calculate Occupancy of a Charter Business: Formula, Methods, and Strategies





